Food delivery robots are spreading fast — but can we really trust them with safety, jobs, and privacy? Read the pros, cons, and future outlook.
Table of Contents
Food Delivery Robots Are Cute. Should We Trust Them?
Introduction
Food delivery robots are no longer science fiction — they’re already rolling through city sidewalks, carrying meals from local restaurants to hungry customers. Companies like Serve Robotics, working with Uber Eats, are introducing fleets of small, boxy robots that look harmless, even cute. But beyond the blinking LED “eyes” and quirky names like Courtney or Deandre, important questions remain: Are food delivery robots reliable, safe, and trustworthy?
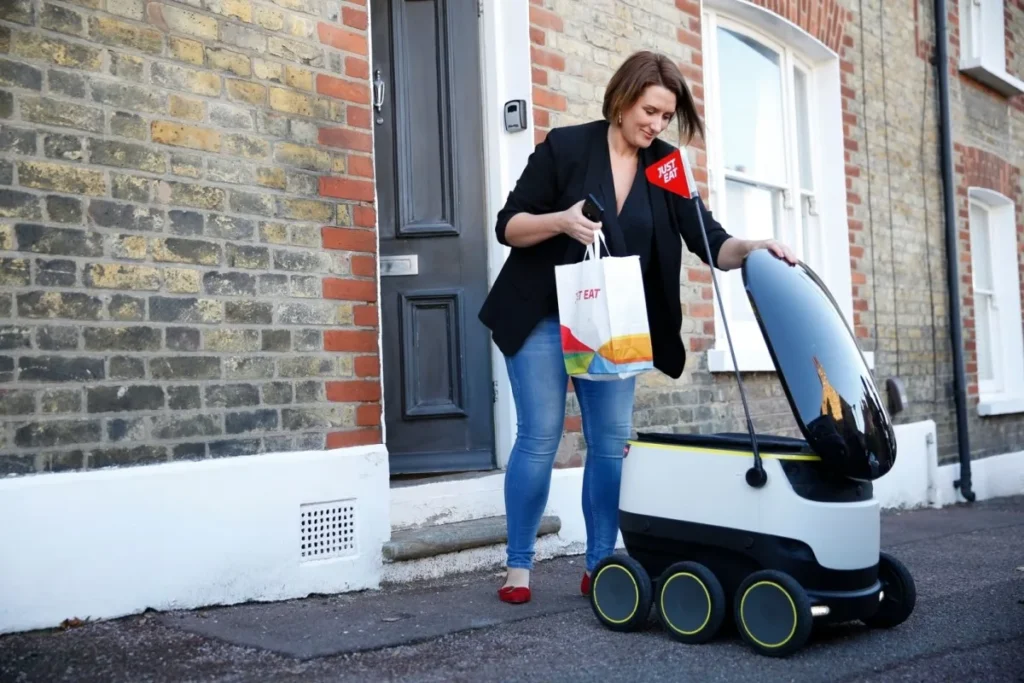

The Rise of Food Delivery Robots in Cities
Serve Robotics has expanded its autonomous couriers into major cities, including Atlanta, Los Angeles, and Chicago. The robots promise faster delivery for short distances, usually under one mile, while reducing traffic and carbon emissions.
- How they work: Equipped with sensors and AI navigation systems, these robots avoid obstacles and travel along sidewalks.
- Partnerships: Uber Eats, Shake Shack, and other food chains are among their early adopters.
- Public reaction: At first, residents were fascinated — snapping photos, making TikToks, and greeting them like futuristic pets.
But as the novelty fades, people are treating them less like “cute tech” and more like moving obstacles.
Why Trust in Robot Couriers Is Still a Concern
Technical Limitations
Despite their promise, food delivery robots often struggle with:
- Navigating uneven sidewalks and crosswalks.
- Sudden speed changes that make them unpredictable.
- Getting stuck in cracks or blocked by pedestrians.
In some cases, customers never receive a robot delivery at all — human couriers still outperform them in speed and reliability.
Privacy and Security Issues
Experts warn that robots equipped with cameras and microphones are not just friendly couriers — they’re data collection devices.
- AI scholar Joanna Bryson highlights risks of corporate surveillance.
- Without regulation, it’s unclear who monitors the safety and ethics of these machines.
Community Acceptance
Robots often appear in neighborhoods without community input. As Edward Ongweso Jr., a technology researcher, points out, the rollout of such devices is more about investor returns than public demand.

The Business Model Behind Delivery Robots
While Serve promotes its robots as environmentally friendly and cost-effective, critics argue the real motivation is economic:
- Robots don’t need salaries or tips.
- Investors benefit from reducing human delivery jobs.
- “Humanizing” robots with names and lights makes communities more accepting.
Ultimately, they’re not community helpers — they’re part of a growing AI-driven logistics business model.
Benefits of Food Delivery Robots
To balance the skepticism, there are potential upsides:
- Lower delivery costs — no tipping required.
- Reduced emissions — compared to cars or motorcycles.
- Convenience — especially for short-distance food orders.
- Innovation driver — accelerates AI adoption in smart cities.
However, these benefits come with trade-offs in safety, jobs, and ethical regulation.
Should We Trust Them?
Trust in food delivery robots depends on three key factors:
- Transparency → Companies must disclose how data is collected and stored.
- Regulation → Governments should create standards for safety, privacy, and accountability.
- Performance → Until robots prove they can deliver reliably and safely, skepticism will remain healthy.
FAQs About Food Delivery Robots
Q1: How do food delivery robots work?
Food delivery robots use AI-powered navigation, GPS, and sensors to travel sidewalks, avoid obstacles, and deliver meals within short distances.
Q2: Are food delivery robots safe?
While generally safe, robots sometimes block sidewalks or malfunction. Without proper regulation, long-term safety remains uncertain.
Q3: Do delivery robots replace human jobs?
Yes, to some extent. Companies reduce the need for human drivers, potentially affecting gig workers who depend on food delivery income.
Q4: Can food delivery robots be hacked?
Like any connected device, they are vulnerable to cybersecurity threats if not properly secured by manufacturers.
Q5: Are robot deliveries cheaper for customers?
Usually, yes. Since robots don’t require tips, they can lower final delivery costs.
Conclusion
Food delivery robots like Courtney may look playful and futuristic, but their presence raises serious concerns about safety, privacy, and jobs. While they offer convenience and eco-friendly benefits, they’re ultimately a business model powered by AI and investment — not friendly neighbors.
👉 What do you think? Should robots deliver your next meal, or should we keep relying on humans for this essential job? Share your thoughts in the comments!